Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Modeling Radiation in a Headlamp Using the Monte Carlo Method#
This example solves for the radiative and conductive heat transfer within a car headlamp exposed to the sun’s rays to determine the severity of any hotspots that form. It uses a Monte Carlo radiation model and the pressure-based solver. This is based on the Fluent tutorial titled “Using the Monte Carlo Radiation Model”.
Workflow tasks
The Modeling Radiation Using the Monte Carlo Method example guides you through these tasks:
Creation of a mesh using the Watertight Geometry workflow.
Setting up a Monte Carlo radiation model.
Creation of materials with thermal and radiation properties.
Setting boundary conditions for heat transfer and radiation calculations.
Calculating a solution using the pressure-based solver.
Problem description
The problem considers the headlamp of a parked car exposed to sunlight. The lens focuses incoming radiation onto the internal components of the headlamp, producing thermal hotspots that could cause damage due to thermal stresses or material degradation.
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_path = '_static/radiation_headlamp_thumbnail.png'
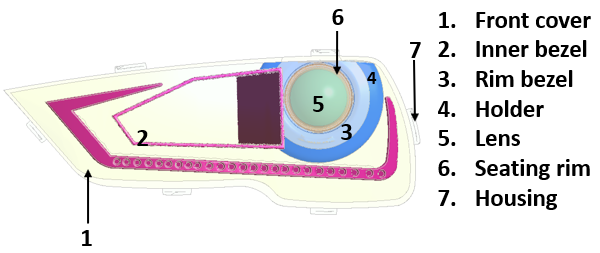
Example Setup#
Before you can use the watertight geometry meshing workflow, you must set up the example and initialize this workflow.
Perform required imports#
Perform required imports, which includes downloading and importing the geometry files.
import ansys.fluent.core as pyfluent
from ansys.fluent.core import examples
headlamp_spaceclaim_file, headlamp_pmdb_file = [
examples.download_file(
f, "pyfluent/radiation_headlamp", save_path=pyfluent.EXAMPLES_PATH
)
for f in ["headlamp.scdoc", "headlamp.pmdb"]
]
Launch Fluent#
Launch Fluent as a service in meshing mode with single precision running on four processors.
meshing = pyfluent.launch_fluent(
precision="single",
processor_count=4,
mode="meshing",
cwd=pyfluent.EXAMPLES_PATH,
)
Initialize workflow#
Initialize the watertight geometry meshing workflow.
meshing.workflow.InitializeWorkflow(WorkflowType="Watertight Geometry")
Watertight geometry meshing workflow#
The fault-tolerant meshing workflow guides you through the several tasks that follow.
Import CAD and set length units#
Import the CAD geometry and set the length units to millimeters.
geo_import = meshing.workflow.TaskObject["Import Geometry"]
geo_import.Arguments.set_state(
{
"FileName": headlamp_pmdb_file,
"LengthUnit": "mm",
}
)
geo_import.Execute()
Add local sizing#
Add local sizing controls to the geometry.
local_sizing = meshing.workflow.TaskObject["Add Local Sizing"]
local_sizing.Arguments.set_state(
{
"AddChild": "yes",
"BOIControlName": "boi_lens",
"BOIExecution": "Body Of Influence",
"BOIFaceLabelList": ["boi"],
"BOISize": 2,
}
)
local_sizing.AddChildAndUpdate()
local_sizing.Arguments.set_state(
{
"AddChild": "yes",
"BOIControlName": "bodysize_lens",
"BOIExecution": "Body Size",
"BOIFaceLabelList": ["lens"],
"BOISize": 2,
}
)
local_sizing.AddChildAndUpdate()
Generate surface mesh#
Generate the surface mesh.
surface_mesh_gen = meshing.workflow.TaskObject["Generate the Surface Mesh"]
surface_mesh_gen.Arguments.set_state(
{
"CFDSurfaceMeshControls": {
"MinSize": 1,
"MaxSize": 40,
}
}
)
surface_mesh_gen.Execute()
Improve surface mesh#
Improve the surface mesh.
surface_mesh_gen.InsertNextTask(CommandName="ImproveSurfaceMesh")
meshing.workflow.TaskObject["Improve Surface Mesh"].Execute()
Describe geometry#
Describe geometry and define the fluid region.
describe_geo = meshing.workflow.TaskObject["Describe Geometry"]
describe_geo.Arguments.set_state(
{
"SetupType": "The geometry consists of both fluid and solid regions \
and/or voids",
"CappingRequired": "No",
"WallToInternal": "No",
"InvokeShareTopology": "No",
"Multizone": "No",
}
)
describe_geo.Execute()
Update boundaries#
Update the boundaries.
update_bc = meshing.workflow.TaskObject["Update Boundaries"]
update_bc.Arguments.set_state(
{
"BoundaryLabelList": ["rad-input"],
"BoundaryLabelTypeList": ["wall"],
}
)
update_bc.Execute()
Create fluid region#
Create the fluid region.
create_regions = meshing.workflow.TaskObject["Create Regions"]
create_regions.Arguments.set_state({"NumberOfFlowVolumes": 1})
create_regions.Execute()
Update regions#
Update the regions.
meshing.workflow.TaskObject["Update Regions"].Execute()
Boundary layers#
Do not add boundary layers and proceed to the next task.
add_boundary_layers = meshing.workflow.TaskObject["Add Boundary Layers"]
add_boundary_layers.Arguments.set_state({"AddChild": "no"})
add_boundary_layers.Execute()
Generate volume mesh#
Generate the volume mesh, which consists of setting properties for the volume mesh.
volume_mesh_gen = meshing.workflow.TaskObject["Generate the Volume Mesh"]
volume_mesh_gen.Arguments.set_state(
{
"VolumeMeshPreferences": {
"PolyFeatureAngle": 40,
},
},
)
volume_mesh_gen.Execute()
Check mesh in meshing mode#
Check the mesh in meshing mode.
meshing.tui.mesh.check_mesh()
Save mesh file#
Save the mesh file (headlamp.msh.h5).
meshing.tui.file.write_mesh("headlamp.msh.h5")
Solve and postprocess#
Once you have completed the watertight geometry meshing workflow, you can solve and postprocess the results.
Switch to solution mode#
Switch to solution mode. Now that a high-quality mesh has been generated using Fluent in meshing mode, you can switch to solver mode to complete the setup of the simulation.
solver = meshing.switch_to_solver()
Enable energy and viscosity models#
Set up the energy and viscosity models.
models = solver.setup.models
models.energy.enabled = True
models.viscous.model = "laminar"
Set up radiation model#
Set up the Monte Carlo radiation model. The number of histories is set to 10 million in order to reduce computation time, but this may need to be increased to obtain accurate results.
radiation = models.radiation
radiation.model = "monte-carlo"
radiation.monte_carlo.number_of_histories = 1e7
radiation.solve_frequency.iteration_interval = 20
Define materials#
Create materials to represent the glass and plastic parts of the headlamp. To demonstrate two different methods of creating materials through the settings API, we will create glass using a dictionary and plastic using dot syntax.
# --- Properties of glass ---
# Density: 2650 [kg/m^3]
# Specific heat capacity: 1887 [J/(kg K)]
# Thermal conductivity: 7.6 [W/(m K)]
# Absorption coefficient: 5.302
# Refractive index: 1.4714
glass = solver.setup.materials.solid.create("glass")
glass.set_state(
{
"chemical_formula": "",
"density": {
"option": "constant",
"value": 2650,
},
"specific_heat": {
"option": "constant",
"value": 1887,
},
"thermal_conductivity": {
"option": "constant",
"value": 7.6,
},
"absorption_coefficient": {
"option": "constant",
"value": 5.302,
},
"refractive_index": {
"option": "constant",
"value": 1.4714,
},
}
)
# --- Properties of plastic ---
# Density: 1545.3 [kg/m^3]
# Specific heat capacity: 2302 [J/(kg K)]
# Thermal conductivity: 0.316 [W/(m K)]
plastic = solver.setup.materials.solid.create("plastic")
plastic.chemical_formula = ""
plastic.density.value = 1545.3
plastic.specific_heat.value = 2302
plastic.thermal_conductivity.value = 0.316
plastic.absorption_coefficient.value = 0
plastic.refractive_index.value = 1
Cell Zone Conditions#
Set the cell zone conditions for the bezel and the lens.
solver.setup.cell_zone_conditions.solid["bezel"].material = "plastic"
solver.setup.cell_zone_conditions.copy(
from_="bezel",
to=[
"holder",
"housing",
"inner-bezel",
"reflector",
"rim-bezel",
"seating-steel-rim",
],
)
lens_cellzone_conds = solver.setup.cell_zone_conditions.solid["lens"]
lens_cellzone_conds.material = "glass"
lens_cellzone_conds.radiating = True
Boundary Conditions#
Set the boundary conditions.
# --- Set up bezel-enclosure BC ---
# Material: plastic
# BC type: opaque
# Internal emissivity: 1
# Diffuse fraction: 1
bezel_enc_bc = solver.setup.boundary_conditions.wall["bezel-enclosure"]
bezel_enc_bc.material = "plastic"
bezel_enc_bc.radiation_bc = "Opaque"
bezel_enc_bc.in_emiss = 1
bezel_enc_bc.band_diffuse_frac = {"s-": 1}
# Get list of wall zones
bc_state = solver.setup.boundary_conditions.get_state()
# Copy bezel-enclosure BC to all other BCs
solver.setup.boundary_conditions.copy(
from_="bezel-enclosure",
to=bc_state["wall"].keys(),
)
# --- Set up enclosure-lens BC ---
# Material: glass
# BC type: semi-transparent
# Diffuse fraction: 0
enc_lens_bc = solver.setup.boundary_conditions.wall["enclosure-lens"]
enc_lens_bc.material = "glass"
enc_lens_bc.radiation_bc = "Semi Transparent"
enc_lens_bc.band_diffuse_frac = {"s-": 0}
# Copy enclosure-lens BC to other lens boundary
solver.setup.boundary_conditions.copy(
from_="enclosure-lens",
to=["enclosure-lens-shadow"],
)
# --- Set up enclosure-rim-bezel BC ---
# Material: plastic
# BC type: opaque
# Internal emissivity: 0.16
# Diffuse fraction: 0.1
enc_rim_bezel_bc = solver.setup.boundary_conditions.wall["enclosure-rim-bezel"]
enc_rim_bezel_bc.material = "plastic"
enc_rim_bezel_bc.radiation_bc = "Opaque"
enc_rim_bezel_bc.in_emiss = 0.16
enc_rim_bezel_bc.band_diffuse_frac = {"s-": 0.1}
# Copy enclosure-rim-bezel BC to other rim bezel boundaries
solver.setup.boundary_conditions.copy(
from_="enclosure-rim-bezel",
to=[
"enclosure-rim-bezel-shadow",
"holder-rim-bezel",
"holder-rim-bezel-shadow",
"housing-rim-bezel",
"housing-rim-bezel-shadow",
],
)
# --- Set up enclosure:1 (domain boundaries) BC ---
# BC type: temperature
# Temperature: 298.15 [K]
enc1_bc = solver.setup.boundary_conditions.wall["enclosure:1"]
enc1_bc.thermal_bc = "Temperature"
enc1_bc.t = 298.15
# --- Set up radiation input BC ---
# BC type: temperature
# Temperature: 298.15 [K]
# Boundary source: yes
# Direct irradiation: 1200 [W/m^2]
# Radiation direction: (-0.848, 0, -0.53)
rad_inp_bc = solver.setup.boundary_conditions.wall["rad-input"]
rad_inp_bc.thermal_bc = "Temperature"
rad_inp_bc.t = 298.15
rad_inp_bc.mc_bsource_p = True
rad_inp_bc.band_q_irrad = {
"s-": {
"option": "value",
"value": 1200,
}
}
rad_inp_bc.radiation_direction = [-0.848, 0, -0.53]
Set convergence criteria#
Enable residual plots and set the convergence criteria to ‘none’.
solver.tui.solve.monitors.residual.plot("yes")
solver.tui.solve.monitors.residual.criterion_type("3")
Define surface reports#
Define a surface report to find the maximum temperature of the inner bezel, then print the state of the report object.
solver.solution.report_definitions.surface["max-temp"] = {}
max_temp_surf_report = solver.solution.report_definitions.surface["max-temp"]
max_temp_surf_report.surface_names = ["enclosure-inner-bezel"]
max_temp_surf_report.report_type = "surface-facetmax"
max_temp_surf_report.field = "temperature"
max_temp_surf_report.print_state()
Define report plots#
Define a plot of the maximum temperature.
solver.solution.monitor.report_plots["max-temp-rplot"] = {}
max_temp_rplot = solver.solution.monitor.report_plots["max-temp-rplot"]
max_temp_rplot.report_defs = "max-temp"
max_temp_rplot.print = True
Save case file#
Save the case file (headlamp.cas.h5).
solver.file.write(file_name="headlamp.cas.h5", file_type="case")
Initialize flow field#
Initialize the solution.
solver.solution.initialization.initialize()
Solve for 19 iterations#
Solve for 19 iterations. 99 iterations is recommended by the tutorial, but is reduced to 19 for this example for demonstration purposes.
solver.solution.run_calculation.iterate(iter_count=19)
Write final case file and data#
Enable overwrite so that the original case file will be overwritten. Write the final case file and the data.
solver.file.confirm_overwrite = True
solver.file.write(file_name="headlamp.cas.h5", file_type="case-data")
Close Fluent#
Close Fluent.
solver.exit()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.000 seconds)